Metallic Taste in Mouth: Causes and Treatment in Torrevieja
The sensation of metal in the mouth is not just an unpleasant symptom that causes discomfort. In medicine, this condition is called dysgeusia (taste distortion) or parageusia (perversion of taste sensations). It can signal temporary changes in the body or indicate serious pathologies requiring medical intervention. According to data from the Spanish Society of Dentistry (S.E.O.E.) for 2026, about 15% of patients visiting the dentist complain of various taste anomalies, and metallic taste leads this list. At the Ap-denta clinic in Torrevieja, we regularly encounter this problem and know how to help patients regain pure taste sensations.
What is metallic taste and who experiences it?
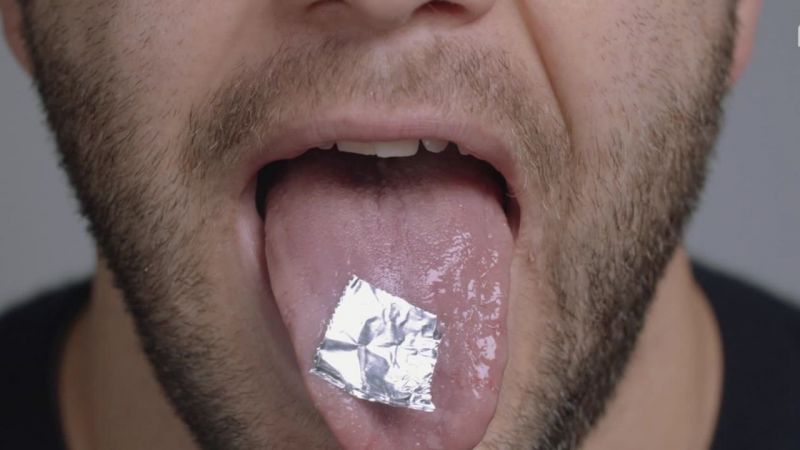
Metallic taste is described by patients as the sensation of having a coin, spoon, or blood in the mouth. It is a subjective perception that does not depend on gender but has age-related characteristics. In children and adolescents, the taste is often associated with teething, wearing braces, or anemia. In adults (25-50 years), the spectrum of causes is wider — from dental problems to gastrointestinal diseases. In elderly people (over 60), dysgeusia often occurs due to taking multiple medications, age-related xerostomia (dry mouth), or wearing removable dentures. Interestingly, women face this problem more often than men due to hormonal fluctuations (pregnancy, menopause).
Why does a metallic taste occur in the mouth?
The mechanism of taste appearance is related to irritation of the taste buds on the tongue, which react to chemical substances. Normally, we distinguish between sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami. When metal ions (iron, copper, zinc) enter the oral cavity or when the chemical composition of saliva changes, the receptors send a distorted signal to the brain. Saliva plays a key role: its pH, mineral composition, and viscosity directly influence taste perception. In the hot climate conditions of Torrevieja, where the average annual temperature is high, many patients suffer from dehydration, leading to saliva thickening and the appearance of metallic taste, especially in the summer months.
Causes of metallic taste in the mouth: dental factors
The most frequent causes are found in the oral cavity. First is insufficient hygiene. Plaque on teeth and tongue, decomposing food residues create a favorable environment for bacteria, whose metabolic products can give a metallic tone. Inflammatory periodontal diseases (gingivitis, periodontitis) lead to gum bleeding. Blood contains iron ions, and even micro-amounts of blood mixed with saliva cause the characteristic taste. Glossitis (inflammation of the tongue) affects the taste buds, disrupting their function. Caries and pulpitis can also be sources of bad breath and taste.
Galvanic syndrome: when metals react with each other
Galvanic syndrome (galvanism) deserves special attention. This condition occurs when different metals are present in the mouth. For example, an old amalgam filling (containing silver, copper, tin, mercury) and a new crown made of cobalt-chromium alloy or a titanium implant. In saliva, which is an electrolyte, these metals form a galvanic pair. A potential difference and microcurrents arise, which not only produce a persistent metallic taste but can cause burning, dryness, headaches. According to studies from the University of Alicante (UA) in 2025, up to 30% of patients with metal constructions in the mouth in the province of Alicante show signs of galvanism. Diagnosis is performed with a special device: a microammeter.
Influence of piercings and orthodontic appliances
Metal jewelry (piercings of the tongue, lips, cheeks) is a direct path to dysgeusia. Low-quality alloys (often containing nickel) oxidize quickly in the aggressive oral environment, especially in contact with acidic foods. The same applies to cheap bracket systems or metal wires. For patients with orthodontic appliances in Torrevieja, we recommend meticulous hygiene and avoiding foods that provoke oxidation (sodas, citrus juices in large quantities). Quality medical alloys (German, Swiss) oxidize significantly less.
Non-dental causes
Metallic taste is often a marker of somatic diseases. Iron deficiency anemia is a classic cause: low hemoglobin makes the body perceive tastes differently. Gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis with low acidity, reflux, liver and gallbladder diseases) can alter saliva composition and cause burping with taste. Neurological disorders (facial nerve damage), diabetes mellitus, kidney diseases, ENT pathologies (sinusitis, tonsillitis) — all are possible causes. Taking certain medications (antibiotics, antihistamines, blood pressure medications, metformin) also produces a side effect in the form of metallic taste.
Influence of environment and climate in Torrevieja
Living conditions on the Costa Blanca leave their mark. High air temperature and low humidity in summer lead to rapid dehydration, decreased salivation, and concentration of salts in saliva, which can cause taste. Hard tap water, characteristic of many areas of Spain, including Torrevieja, contains elevated amounts of minerals (calcium, magnesium, iron). Consuming this water without filtering can provoke the symptom. Additionally, proximity to the sea and dietary particularities (abundance of seafood rich in iodine and trace elements) can also influence taste perception in sensitive individuals.
Diagnosis: which doctor to see?
The first step is to visit the dentist. At the Ap-denta clinic, we conduct a thorough examination of the oral cavity, assessing the condition of teeth, gums, fillings, crowns, and implants. Measurement of galvanic currents is mandatory if galvanism is suspected. If necessary, we prescribe a panoramic X-ray (OPG) to assess hidden inflammatory processes. If the dental cause is excluded, the patient is referred to a general practitioner, who may order tests: complete blood count (to rule out anemia), biochemistry (liver tests, glucose), ferritin, vitamin B12, thyroid hormones. Consultation with a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, or neurologist may be required.
How to get rid of metallic taste in the mouth: treatment
Treatment directly depends on the identified cause. For dental problems: professional hygiene, treatment of caries and gum inflammation, replacement of amalgam fillings with composite, replacement of metal constructions (crowns, dentures) with metal-free ones (zirconium dioxide, ceramic) to eliminate galvanism. For glossitis — anti-inflammatory therapy. For anemia — iron supplements and dietary correction. For gastrointestinal diseases — treatment with a gastroenterologist (diet, antacids, enzymes). If the cause is medications, the doctor may adjust therapy by finding an analogue. It is important to normalize fluid intake, especially in the hot climate of Torrevieja.
Prevention: dentist's advice
Preventing the problem is easier than treating it. Main preventive measures include: meticulous oral hygiene (brushing twice daily, using an irrigator, tongue cleaning with a scraper), regular dental visits (every 6 months), smoking cessation, and limiting alcohol. It is recommended to use quality water filters to reduce mineral and chlorine intake. In the diet, limit foods that provoke oxidation: carbonated drinks, acidic fruits and juices in excess, spicy foods. Replace metal cookware (especially aluminum) with glass, ceramic, or quality non-stick coated ones.
Types and localization: what does the taste indicate?
The character of the taste and its localization can suggest the cause. Taste on the tip of the tongue is often related to stomatitis or local irritation. Taste at the base of the tongue may indicate gastroesophageal reflux (acid backflow from the stomach). Constant taste, independent of food, often indicates galvanism or systemic disease. Morning taste can be a sign of reflux or gallbladder problems. Taste after eating — reaction to certain foods or low-quality dentures.
Conclusion from Ap-denta clinic specialist in Torrevieja
Dentist at Ap-denta clinic, Torrevieja
Metallic taste in the mouth is a symptom that cannot be ignored. It can be a harmless consequence of dehydration on a hot day at Torrevieja beach, or it can signal serious disorders in the body, from galvanic syndrome to hidden anemia or liver pathology. In our clinic, we use a comprehensive approach to diagnosis: we start with a thorough dental examination and, if necessary, involve related specialists. Modern equipment allows us to accurately determine causes, and the use of biocompatible materials (zirconium dioxide, ceramic) helps eliminate the problem of galvanism forever. If this symptom bothers you, do not postpone your visit. Book a consultation at Ap-denta in Torrevieja — we will help you regain the pleasure of pure taste.