White Tongue: A Body Signal from Torrevieja
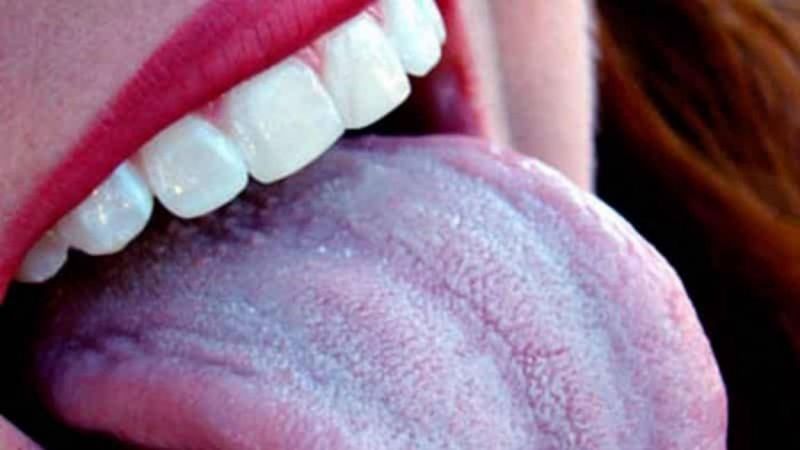
White tongue is a phenomenon that periodically affects almost every resident of the Costa Blanca, from infants to adults. In the Mediterranean climate of Torrevieja, with its high humidity and intense sun, the mucous membranes can be particularly sensitive. It is crucial to understand the difference between harmless morning coating and a symptom requiring dental or medical attention.
What Does a White Tongue Mean: Normal or Pathological?
Physiological, or normal, white tongue coating is a thin, translucent, easily removable layer. It is especially noticeable in the morning due to reduced nighttime salivary flow and slowed self-cleaning. In infants, this coating is often related to feeding. Pathological coating is dense, often with a cheesy or membranous consistency, difficult to remove, and quickly returns. Its key marker is persistence throughout the day. According to 2025-2026 medical reviews, persistent coating can indicate local or systemic disorders.
Main Causes of White Tongue Formation
The etiology of this symptom is diverse. In clinical practice, it is divided into several groups. Dental causes are the most common: oral candidiasis (thrush), various forms of stomatitis, poor oral hygiene, and xerostomia (dry mouth). Gastroenterological factors include gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gastritis, and intestinal microbiota imbalances (SIBO, dysbiosis). Infectious diseases (scarlet fever, tonsillitis) and systemic conditions (diabetes mellitus, iron or B-vitamin deficiency) also manifest as a coated tongue. In this coastal climate, the role of dehydration should be noted.
Diagnosing White Coating: 2026 Modern Protocols
The diagnostic algorithm in Spanish clinical practice begins with a dental consultation. The specialist performs a visual examination, assessing the coating's characteristics: location (root, tip, lateral borders), consistency, color, and the state of the papillae. A detailed medical history is taken, including diet, hygiene habits, chronic diseases, and medication. If systemic causes are suspected, a consultation with a gastroenterologist or general practitioner may be recommended. Laboratory diagnostics may include a microbiological culture of a scraping to identify Candida albicans, as well as complete blood counts and biochemical analyses.
Modern Treatment: From Hygiene to Systemic Therapy
Treatment is strictly etiotropic, meaning it targets the identified cause. For candidiasis, topical and/or systemic antifungals (based on clotrimazole, nystatin, fluconazole) are used according to protocol. Stomatitis requires local antiseptics (chlorhexidine, cetylpyridinium agents) and anti-inflammatories. If the cause is digestive diseases, the treatment plan is determined by a gastroenterologist and may include diet, probiotics, or proton pump inhibitors. Regardless of the cause, basic local hygiene is essential: cleaning the tongue with a scraper twice daily, using an irrigator, and mouthwashes.
Prevention and Conclusion from Ap-denta Specialists
Preventing pathological coating is comprehensive. It includes impeccable oral hygiene, a balanced diet low in sugar, maintaining proper hydration (especially relevant in the warm Costa Blanca climate), smoking cessation, and regular dental check-ups at least twice a year. Remember: the tongue is a mirror of your overall health. A persistent, dense white coating, especially if accompanied by burning, dryness, or halitosis, is a valid reason for professional diagnosis. Timely consultation allows for quick resolution of the local issue or early detection of a more serious underlying disease.



